Big Data¶
Reference:
-
Data Analysis with Python and PySpark, ISBN: 9781617297205
-
Hadoop: The Definitive Guide 4th Edition, ISBN: 9781491901632
Glossary¶
- RDD
- Resilient Distributed Dataset
- 不可变的分布式对象集合
- After Spark 2.0, RDDs are replaced by Dataset, which is strongly-typed like an RDD, but with richer optimizations under the hood. We highly recommend you to switch to use Dataset, which has better performance than RDD.
- Hadoop 三个组成部分
- MapReduce: 分布式运算程序的编程框架
- HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System,Hadoop 分布式文件系统
- YARN: Yet Another Resource Negotiator,资源调度平台
- ETL
- Extract-Transform-Load
- 是一个数据流 pipeline 的控制技术
- 是将大量的原始数据经过提取 extract、转换 transform、加载 load 到目标存储数据仓库的过程
- Data Lakes 数据湖,Big Data Warehouse 大数据仓库
- UDF: User Defined Functions,PySpark 自定义函数
- REPL: Python解释器的交互式模式
- Read: 读取用户输入
- Eval: 执行输入内容
- Print: 执行输入内容
- Loop: 执行输入内容
- 文件格式
- CSV: Comma Separated Values 逗号分隔值
- JSON: JavaScript Object Notation
- ORC: Optimized Row Columnar
- Parquet: Column-oriented data file format
Spark & PySpark¶
Definition¶
- Spark is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. 用于大规模数据处理的统一分析引擎
- Scaling out instead of scaling up. 将数据 split 到2个中型计算机,而不是使用1个大型计算机
- Spark itself is coded in Scala. Python codes have to be translated to and from JVM instructions.
- 代替 Hadoop 中的 MapReduce 框架
Data Factory:
- 在 Spark cluster 中每个 workbench / computer 会分配一些 workers / executors
- 这些 workers / executors 中有一个 master,对程序的效率很重要
Spark 算子 / RDD Operations 可以被归为2类:
-
Actions (IO)
-
via the
showandwritemethods -
Printing information on the screen
-
Writing data to a hard drive or cloud bucket
-
-
Transformations (Lazy)
- Adding a column to a table
- Performing an aggregation according to certain keys
- Computing summary statistics on a data set
- Training a Machine Learning model on some data
-
Lazy computation model, will take this to the extreme and will avoid performing data work until an action triggers the computation chain. 所有的 Transformations 都是 Lazy 操作,只记录需要进行的转换,并不会马上执行,只有遇到 Actions 操作时才会真正启动计算过程并进行计算。
-
Reading data, although clearly being I/O, is considered a transformation by Spark.
QuickStart: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/quick-start.html
- Install:
brew install openjdk@17 apache-spark - Launch the PySpark shell in IPython:
PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON=ipython pyspark - Spark’s primary abstraction is a distributed collection of items called a Dataset. Datasets can be created from Hadoop InputFormats (such as HDFS files) or by transforming other Datasets. All Datasets in Python are Dataset[Row], and we call it
DataFrame. - Caching: Spark also supports pulling data sets into a cluster-wide in-memory cache. This is very useful when data is accessed repeatedly, such as when querying a small “hot” dataset or when running an iterative algorithm like PageRank.
Cluster Manager¶
Cluster Mode Overview: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/cluster-overview.html
Spark applications run as independent sets of processes on a cluster, coordinated by the SparkContext object in your main program (called the driver program).
工作原理:
-
在 cluster 上运行时,
SparkContext可以连接到不同类型的 cluster managers 上-
Cluster Manager 类型:
- Standalone: Spark’s own standalone cluster manager
- Apache Mesos: Deprecated
- Hadoop YARN: The resource manager in Hadoop 3
- Kubernetes: An open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications
-
Cluster Manager 作用:Allocate resources across applications
-
Deploy mode:
-
-
建立连接后,Spark 会获取 executors
- Executors 在 cluster 里的 worker nodes 当中
- Executors are processes that run computations and store data for your application.
- Each application gets its own executor processes.
-
SparkContext将应用程序代码 (JAR or Python files) 发送给 executors -
SparkContext将 task 发送给 executors 运行- Each job gets divided into smaller sets of tasks called stages that depend on each other (similar to the map and reduce stages in MapReduce).
RDD¶
RDD Programming Guide: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/rdd-programming-guide.html
Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD) is a fault-tolerant collection of elements partitioned across the nodes of the cluster, and can be operated on in parallel.
- RDDs are created by starting with a file in the Hadoop file system (or any other Hadoop-supported file system), or an existing Scala collection in the driver program, and transforming it.
- Users may also ask Spark to persist an RDD in memory, allowing it to be reused efficiently across parallel operations.
- Finally, RDDs automatically recover from node failures.
Parallelized Collections:
-
Created by calling
SparkContext’sparallelizemethod on an existing iterable or collection in your driver program. We can calldistData.reduce(lambda a, b: a + b)to add up the elements of the list.In [4]: sc = spark.sparkContext In [6]: data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] In [7]: distData = sc.parallelize(data) In [8]: distData Out[8]: ParallelCollectionRDD[0] at readRDDFromFile at PythonRDD.scala:289 In [9]: distData.reduce(lambda a, b: a + b) Out[9]: 15 In [10]: distData.reduce(lambda a, b: a * b) Out[10]: 120 -
Spark will run one task for each partition of the cluster. Typically you want 2-4 partitions for each CPU in your cluster.
-
Normally, Spark tries to set the number of partitions automatically based on your cluster. However, you can also set it manually by passing it as a second parameter to
parallelize(e.g.sc.parallelize(data, 10)).
Shared Variables:
Spark supports two types of shared variables that can be used in parallel operations.
- Broadcast variables can be used to cache a read-only value in memory on all nodes.
- Accumulators are variables that are only “added” to, such as counters and sums.
Spark SQL¶
Spark SQL, DataFrames and Datasets Guide: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/sql-programming-guide.html
Misc¶
- Example: https://spark.apache.org/examples.html
- Submitting applications (
spark-submit)- https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/submitting-applications.html
--master local[K]: Run Spark locally with K worker threads (ideally, set this to the number of cores on your machine).
Performance¶
Web UI: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/web-ui.html
Monitoring and Instrumentation: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/monitoring.html
PySpark API¶
SparkSession¶
API: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/python/reference/pyspark.sql/spark_session.html
The entry point to programming Spark with the Dataset and DataFrame API. A SparkSession can be used to create DataFrame, register DataFrame as tables, execute SQL over tables, cache tables, and read parquet files. To create a Spark session, you should use SparkSession.builder attribute.
In [1]: from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
In [2]: spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()
24/01/29 16:19:10 WARN Utils: Your hostname, mbp.local resolves to a loopback address: 127.0.0.1; using 192.168.226.124 instead (on interface en0)
24/01/29 16:19:10 WARN Utils: Set SPARK_LOCAL_IP if you need to bind to another address
Setting default log level to "WARN".
To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel).
24/01/29 16:19:40 WARN NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
SparkSession is a super-set of SparkContext. It wraps the SparkContext and provides functionality for interacting with SparkContext data in a distributed fashion. 注意这里 spark.sparkContext 是小写字母
In [3]: spark.sparkContext
Out[3]: <SparkContext master=local[*] appName=pyspark-shell>
-
设置日志等级:
SparkContext.setLogLevel(logLevel: str) → None,默认WARN -
Eager Evaluation: when you want your data frames to be evaluated after each transformation.
.config("spark.sql.repl.eagerEval.enabled", "True")- Spark Configuration: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/configuration
-
Reading data into a data frame is done through
DataFrameReaderthe object, which we can access throughspark.read.In [12]: spark.read Out[12]: <pyspark.sql.readwriter.DataFrameReader at 0x1074cb810> In [13]: print(dir(spark.read)) ['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_df', '_jreader', '_set_opts', '_spark', 'csv', 'format', 'jdbc', 'json', 'load', 'option', 'options', 'orc', 'parquet', 'schema', 'table', 'text']
DataFrame¶
API: https://spark.apache.org/docs/3.5.0/api/python/reference/pyspark.sql/dataframe.html
A distributed collection of data grouped into named columns. In the RDD, each record is processed independently. With the data frame, we work with its columns, performing functions on them.
-
printSchema(level: Optional[int] = None) → NonePrints out the schema in the tree format. Optionally allows to specify how many levels to print if schema is nested.
In [15]: df = spark.createDataFrame([(1, (2,2))], ["a", "b"]) In [16]: df.printSchema(2) root |-- a: long (nullable = true) |-- b: struct (nullable = true) | |-- _1: long (nullable = true) | |-- _2: long (nullable = true) -
show(n: int = 20, truncate: Union[bool, int] = True, vertical: bool = False) → NonePrints the first
nrows to the console.In [23]: df = spark.createDataFrame([ ...: (14, "Tom"), (23, "Alice"), (16, "Bob")], ["age", "name"]) In [24]: df.show(n=2, truncate=3) +---+----+ |age|name| +---+----+ | 14| Tom| | 23| Ali| +---+----+ only showing top 2 rows -
select(*cols: ColumnOrName) → DataFrameProjects a set of expressions and returns a new DataFrame.
[ins] In [15]: df = spark.createDataFrame([ ...: (2, "Alice"), (5, "Bob")], schema=["age", "name"]) [ins] In [16]: df.select(df.name, (df.age + 10).alias('age')).show() +-----+---+ | name|age| +-----+---+ |Alice| 12| | Bob| 15| +-----+---+
Column¶
API: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/python/reference/pyspark.sql/column.html
A column in a DataFrame.
-
alias(*alias: str, **kwargs: Any) → pyspark.sql.column.ColumnWhen performing transformation on your columns, PySpark will give a default name to the resulting column.
[ins] In [35]: sf.split(sf.col("value"), " ") Out[35]: Column<'split(value, , -1)'> [ins] In [36]: sf.split(sf.col("value"), " ").alias("words") Out[36]: Column<'split(value, , -1) AS words'>
Functions¶
import pyspark.sql.functions as sf
API: https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/python/reference/pyspark.sql/functions.html
PySpark uses a translation layer to call JVM functions for its core functions. From Spark 3.5:
-
col(col: str) → pyspark.sql.column.ColumnReturns a Column based on the given column name.
-
split(str: ColumnOrName, pattern: str, limit: int = - 1) → pyspark.sql.column.ColumnSplits str around matches of the given pattern. The regex string should be a Java regular expression.
-
explode(col: ColumnOrName) → pyspark.sql.column.ColumnReturns a new row for each element in the given array or map. Uses the default column name col for elements in the array and key and value for elements in the map unless specified otherwise.
[ins] In [54]: from pyspark.sql import Row [ins] In [55]: row = Row(a=1, intlist=[1,2,3], mapfield={"a": "b"}) [ins] In [56]: df = spark.createDataFrame([row, row]) [ins] In [57]: df.show() +---+---------+--------+ | a| intlist|mapfield| +---+---------+--------+ | 1|[1, 2, 3]|{a -> b}| | 1|[1, 2, 3]|{a -> b}| +---+---------+--------+ [ins] In [58]: df.select(sf.explode('intlist')).show() +---+ |col| +---+ | 1| | 2| | 3| | 1| | 2| | 3| +---+ [ins] In [59]: df.select(sf.explode('mapfield')).show() +---+-----+ |key|value| +---+-----+ | a| b| | a| b| +---+-----+
Hive¶
Common HiveQL¶
Documents¶
-
HiveQL Data Definition Language (DDL) HiveQL 语法
-
Hive Operators 运算符
- https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/Hive+Operators
A <> B: NULL if A or B is NULL, TRUE if expression A is NOT equal to expression B, otherwise FALSE.
-
Hive Data Types 数据类型
- https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+Types
- INT/INTEGER (4-byte signed integer, from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647)
-
Managed vs. External Tables 内部表和外部表的区别
- https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/Managed+vs.+External+Tables
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/580296016
- 内部表:Use managed tables when Hive should manage the lifecycle of the table, or when generating temporary tables.
- 外部表:Use external tables when files are already present or in remote locations, and the files should remain even if the table is dropped.
-
Hive Operators and User-Defined Functions (UDFs)
- https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+UDF
regexp_replace(string INITIAL_STRING, string PATTERN, string REPLACEMENT)substr(string|binary A, int start)md5(string/binary)- Calculates an MD5 128-bit checksum for the string or binary (as of Hive 1.3.0). The value is returned as a string of 32 hex digits, or NULL if the argument was NULL. Example:
md5('ABC') = '902fbdd2b1df0c4f70b4a5d23525e932'.
- Calculates an MD5 128-bit checksum for the string or binary (as of Hive 1.3.0). The value is returned as a string of 32 hex digits, or NULL if the argument was NULL. Example:
if(boolean testCondition, T valueTrue, T valueFalseOrNull)- Returns valueTrue when testCondition is true, returns valueFalseOrNull otherwise.
from_unixtime(bigint unixtime[, string pattern])- Converts a number of seconds since epoch (1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC) to a string representing the timestamp of that moment in the current time zone(using config "hive.local.time.zone") using the specified pattern.
- 时区问题:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38251332/article/details/122101966
-
Hive CLI
- https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+Cli
hive -i <filename>, Initialization SQL file- Running an initialization script before entering interactive mode
hive -f <filename>, SQL from files- Running a script non-interactively from local disk or from a Hadoop supported filesystem
hive -i <init_sql> -f <script_sql>- 传入参数variable
hive --hivevar queue=default
-
StatsDev
- https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/StatsDev
- https://www.cnblogs.com/coco2015/p/15870532.html,当
COUNT(*)为 0 时: ANALYZE TABLE <table_name> [PARTITION(col=val)] COMPUTE STATISTICS;更新 metastore- 或者
SET hive.compute.query.using.stats=false; DESC EXTENDED <table_name> [PARTITION(col=val)];
-
Beeline CLI
- https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/HiveServer2+Clients
beeline -u <database_url>, The JDBC URL to connect tobeeline -i <file>, The init files for initializationbeeline --outputformat=csv2--outputformat=[table/vertical/csv/tsv/dsv/csv2/tsv2]- Format mode for result display. Default is table.
--silent=[true/false]- Reduce the amount of informational messages displayed (true) or not (false).
grep -v '^$' <csv_file>删掉空行
-
时区问题
- Hive 版本 3.1.4
FROM_UNIXTIME()和UNIX_TIMESTAMP()都是按 UTC 时区来,和中国时区差8小时 - 问题描述:https://www.baifachuan.com/posts/2f3913c8.html
- 源码地址:https://archive.apache.org/dist/hadoop/core/hadoop-3.1.4/
- Hive 版本 3.1.4
-
Hive Configuration Properties
-
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/Configuration+Properties
-
设置队列
hive --hivevar queue=<queue_name>-- Set queue to variable SET tez.queue.name = ${queue}; SET mapreduce.job.queuename = ${queue}; SET mapred.job.queue.name = ${queue}; -
合并小文件
-- Merge small files to 128MB, using Tez as execution engine SET hive.merge.tezfiles = true; -- SET hive.merge.sparkfiles = true; SET hive.merge.mapfiles = true; SET hive.merge.mapredfiles = true; SET hive.merge.size.per.task = 128000000; SET hive.merge.smallfiles.avgsize = 128000000; -
Map Reduce config: https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/hadoop-mapreduce-client/hadoop-mapreduce-client-core/mapred-default.xml
- Tez config: https://tez.apache.org/releases/0.8.2/tez-api-javadocs/configs/TezConfiguration.html
-
-
Materialized views
Hadoop¶
File System (FS) CLI¶
Document: https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-common/FileSystemShell.html
- Human-readable file size:
hadoop fs -du -h <path> - Changes the replication factor of a file:
hadoop fs -setrep -w <numReplicas> <path>
Yarn CLI¶
Document: https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YarnCommands.html
- Application
applicationorapp- Get application ID:
yarn app -list -appStates FINISHED | grep 'chenlu' yarn app -list -appStates FAILED | grep 'chenlu'- Application ID:
application_xxx
- Get application ID:
- View application status (start time, finish time)
yarn app -status <app_id>
- List application attempts
- View container ID:
yarn applicationattempt -list <app_id>
- View container ID:
- Dump container log
yarn logs -applicationId <app_id> | lessyarn logs -containerId <container_id> | less
- Kill an application
yarn app -kill <app_id>
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)¶
1 介绍¶
References:
- https://github.com/heibaiying/BigData-Notes/blob/master/notes/Hadoop-HDFS.md
- https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/HdfsDesign.html
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)是 Hadoop 下的分布式文件系统,具有高容错、高吞吐量等特性,可以部署在低成本的硬件上。
2 HDFS 设计原理¶
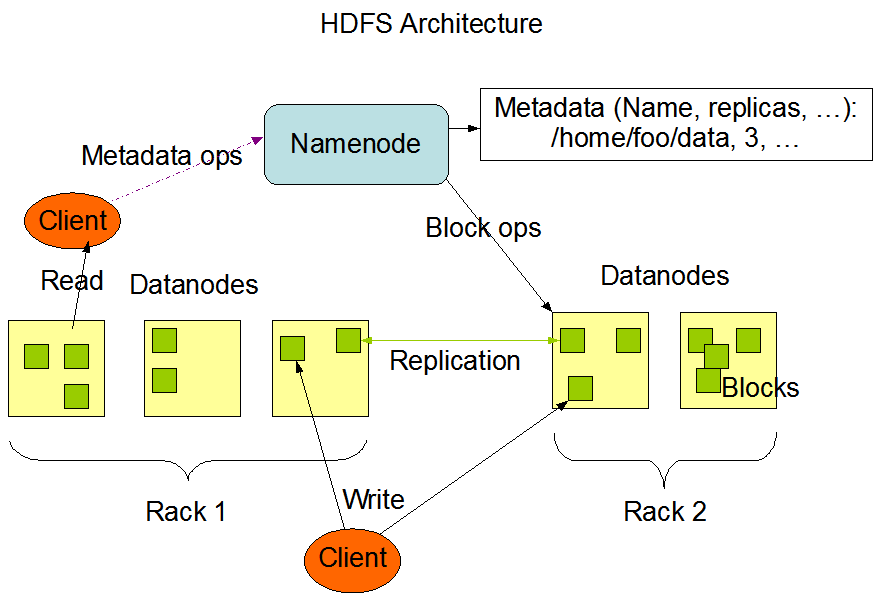
2.1 HDFS 架构¶
HDFS 遵循主/从架构,由单个 NameNode(NN) 和多个 DataNode(DN) 组成:
- NameNode : 负责执行有关
文件系统命名空间的操作,例如打开,关闭、重命名文件和目录等。它同时还负责集群元数据的存储,记录着文件中各个数据块的位置信息。 - DataNode:负责提供来自文件系统客户端的读写请求,执行块的创建,删除等操作。
2.2 文件系统命名空间 The File System Namespace¶
HDFS 的 文件系统命名空间 的层次结构与大多数文件系统类似 (如 Linux), 支持目录和文件的创建、移动、删除和重命名等操作,支持配置用户和访问权限,但不支持硬链接和软连接。NameNode 负责维护文件系统名称空间,记录对名称空间或其属性的任何更改。
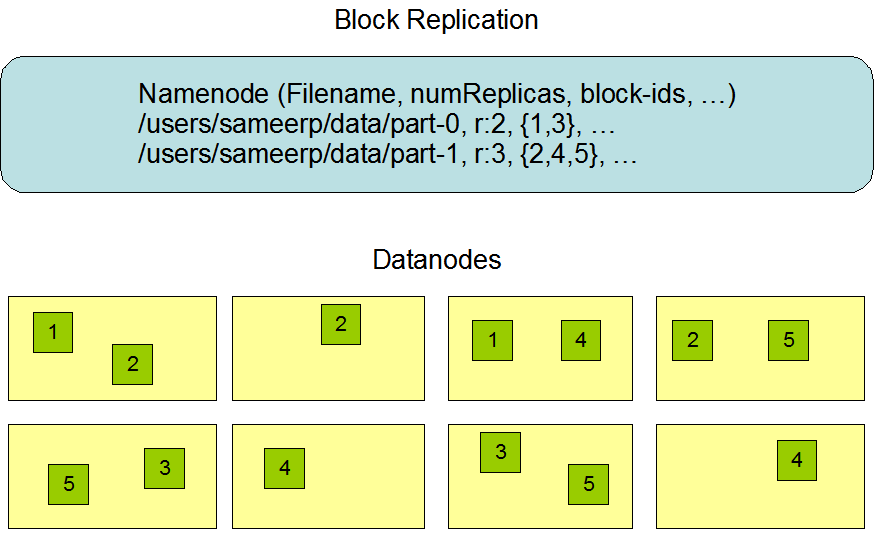
2.3 数据复制 Data Replication¶
由于 Hadoop 被设计运行在廉价的机器上,这意味着硬件是不可靠的,为了保证容错性,HDFS 提供了数据复制机制。HDFS 将每一个文件存储为一系列**块**,每个块由多个副本来保证容错,块的大小和复制因子可以自行配置(默认情况下,块大小是 128M,默认复制因子是 3)。
2.4 数据复制的实现原理¶
大型的 HDFS 实例在通常分布在多个机架的多台服务器上,不同机架上的两台服务器之间通过交换机进行通讯。在大多数情况下,同一机架中的服务器间的网络带宽大于不同机架中的服务器之间的带宽。因此 HDFS 采用机架感知副本放置策略,对于常见情况,当复制因子为 3 时,HDFS 的放置策略是:
在写入程序位于 datanode 上时,就优先将写入文件的一个副本放置在该 datanode 上,否则放在随机 datanode 上。之后在另一个远程机架上的任意一个节点上放置另一个副本,并在该机架上的另一个节点上放置最后一个副本。此策略可以减少机架间的写入流量,从而提高写入性能。
如果复制因子大于 3,则随机确定第 4 个和之后副本的放置位置,同时保持每个机架的副本数量低于上限,上限值通常为 (复制系数 - 1)/机架数量 + 2,需要注意的是不允许同一个 dataNode 上具有同一个块的多个副本。
2.5 副本的选择¶
为了最大限度地减少带宽消耗和读取延迟,HDFS 在执行读取请求时,优先读取距离读取器最近的副本。如果在与读取器节点相同的机架上存在副本,则优先选择该副本。如果 HDFS 群集跨越多个数据中心,则优先选择本地数据中心上的副本。
2.6 架构的稳定性¶
-
心跳机制和重新复制
每个 DataNode 定期向 NameNode 发送心跳消息,如果超过指定时间没有收到心跳消息,则将 DataNode 标记为死亡。NameNode 不会将任何新的 IO 请求转发给标记为死亡的 DataNode,也不会再使用这些 DataNode 上的数据。 由于数据不再可用,可能会导致某些块的复制因子小于其指定值,NameNode 会跟踪这些块,并在必要的时候进行重新复制。
-
数据的完整性
由于存储设备故障等原因,存储在 DataNode 上的数据块也会发生损坏。为了避免读取到已经损坏的数据而导致错误,HDFS 提供了数据完整性校验机制来保证数据的完整性,具体操作如下:
当客户端创建 HDFS 文件时,它会计算文件的每个块的
校验和,并将校验和存储在同一 HDFS 命名空间下的单独的隐藏文件中。当客户端检索文件内容时,它会验证从每个 DataNode 接收的数据是否与存储在关联校验和文件中的校验和匹配。如果匹配失败,则证明数据已经损坏,此时客户端会选择从其他 DataNode 获取该块的其他可用副本。 -
元数据的磁盘故障
FsImage和EditLog是 HDFS 的核心数据,这些数据的意外丢失可能会导致整个 HDFS 服务不可用。为了避免这个问题,可以配置 NameNode 使其支持FsImage和EditLog多副本同步,这样FsImage或EditLog的任何改变都会引起每个副本FsImage和EditLog的同步更新。 -
支持快照
快照支持在特定时刻存储数据副本,在数据意外损坏时,可以通过回滚操作恢复到健康的数据状态。
3 HDFS 的特点¶
-
高容错
由于 HDFS 采用数据的多副本方案,所以部分硬件的损坏不会导致全部数据的丢失。
-
高吞吐量
HDFS 设计的重点是支持高吞吐量的数据访问,而不是低延迟的数据访问。
-
大文件支持
HDFS 适合于大文件的存储,文档的大小应该是是 GB 到 TB 级别的。
-
简单一致性模型
HDFS 更适合于一次写入多次读取 (write-once-read-many) 的访问模型。支持将内容追加到文件末尾,但不支持数据的随机访问,不能从文件任意位置新增数据。
-
跨平台移植性
HDFS 具有良好的跨平台移植性,这使得其他大数据计算框架都将其作为数据持久化存储的首选方案。
附:图解HDFS存储原理¶
说明:以下图片引用自博客:翻译经典 HDFS 原理讲解漫画